The address through which any computer communicates with our computer is simply called an Internet Protocol Address or IP address. For example, If we want to load a web page or we want to download something, we require the address for delivery of that particular file or webpage. That address is called an IP Address.
Types of IP Addresses
1. IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4)
2. IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6)
2. IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6)
IPv4
IPv4 address consists of two things that are the network address and the host address. It stands for Internet Protocol version four. It was introduced in 1981 by DARPA and was the first deployed version in 1982 for production on SATNET and on the ARPANET in January 1983.
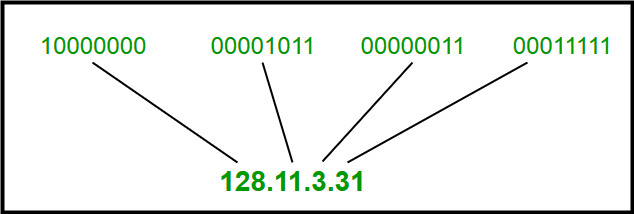
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit integers that have to be expressed in Decimal Notation. It is represented by 4 numbers separated by dots in the range of 0-255, which have to be converted to 0 and 1, to be understood by Computers. For Example, An IPv4 Address can be written as 189.123.123.90.
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit integers that have to be expressed in Decimal Notation. It is represented by 4 numbers separated by dots in the range of 0-255, which have to be converted to 0 and 1, to be understood by Computers. For Example, An IPv4 Address can be written as 189.123.123.90.
IPv4 Address Format
IPv4 Address Format is a 32-bit Address that comprises binary digits separated by a dot (.).
IPv6
IPv6 is based on IPv4 and stands for Internet Protocol version 6. It was first introduced in December 1995 by Internet Engineering Task Force. IP version 6 is the new version of Internet Protocol, which is way better than IP version 4 in terms of complexity and efficiency. IPv6 is written as a group of 8 hexadecimal numbers separated by colon (:). It can be written as 128 bits of 0s and 1s.
IPv6 Address Format
IPv6 Address Format is a 128-bit IP Address, which is written in a group of 8 hexadecimal numbers separated by colon (:).

Benefits of IPv6
The recent Version of IP IPv6 has a greater advantage over IPv4. Here are some of the mentioned benefits:
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 has a 32-bit address length | IPv6 has a 128-bit address length |
| It Supports Manual and DHCP address configuration | It supports Auto and renumbering address configuration |
| In IPv4 end to end, connection integrity is Unachievable | In IPv6 end-to-end, connection integrity is Achievable |
| Island Trading | Helen Bennett |
| It can generate 4.29×109 address space | The address space of IPv6 is quite large it can produce 3.4×1038 address space |
| The Security feature is dependent on the application | IPSEC is an inbuilt security feature in the IPv6 protocol |
| Address representation of IPv4 is in decimal | Address Representation of IPv6 is in hexadecimal |
| Fragmentation performed by Sender and forwarding routers | In IPv6 fragmentation is performed only by the sender |
| In IPv4 Packet flow identification is not available | In IPv6 packet flow identification are Available and uses the flow label field in the header |
| In IPv4 checksum field is available | In IPv6 checksum field is not available |
| It has a broadcast Message Transmission Scheme | In IPv6 multicast and anycast message transmission scheme is available |
| In IPv4 Encryption and Authentication facility not provided | In IPv6 Encryption and Authentication are provided |
| IPv4 has a header of 20-60 bytes. | IPv6 has a header of 40 bytes fixed |
| IPv4 can be converted to IPv6 | Not all IPv6 can be converted to IPv4 |
| IPv4 consists of 4 fields which are separated by addresses dot (.) | IPv6 consists of 8 fields, which are separated by a colon (:) |
| IPv4’s IP addresses are divided into five different classes. Class A , Class B, Class C, Class D , Class E. | IPv6 does not have any classes of the IP address. |
| IPv4 supports VLSM(Variable Length subnet mask). | IPv6 does not support VLSM. |
| Example of IPv4: 66.94.29.13 | Example of IPv6: 2001:0000:3238:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:FEFB |
FAQs
Q.1: Which is Better: IPv4 or IPv6?
Answer:
IPv6 is better than IPv4 as IPv6 is more advanced and has more features than IPv4.
Answer:
IPv6 is better than IPv4 as IPv6 is more advanced and has more features than IPv4.
Q.2: Can we use both IPv4 and IPv6?
Answer:
Yes. We can use both IPv4 and IPV6 in a single machine. There are devices that support dual addressing. When two devices communicate, they agree on which IP Version to use.
Answer:
Yes. We can use both IPv4 and IPV6 in a single machine. There are devices that support dual addressing. When two devices communicate, they agree on which IP Version to use.
Q.3: Which is faster: IPv4 or IPv6?
Answer:
Generally, IPv6 is faster than IPv4. However, when we go to a larger packet size, IPv6 can be slow in some cases.
Answer:
Generally, IPv6 is faster than IPv4. However, when we go to a larger packet size, IPv6 can be slow in some cases.


