JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine, In other words, it is a program/software which takes Java bytecode and converts the byte code (line by line) into machine understandable code.
- JVM(Java Virtual Machine) acts as a run-time engine to run Java applications. JVM is the one that actually calls the main method present in Java code. JVM is a part of the JRE(Java Runtime Environment).
- JVM perform some particular types of operations:
- Loading of code
- Verification of code
- Executing the code
- It provides a run-time environment to the users
ClassLoader
- It is a subsystem of JVM which is used to load class files. It is mainly responsible for three activities.
- Loading
- Linking
- Initialization
Types of Memory Areas Allocated By the JVM:
All these functions take different forms of memory structure. The memory in the JVM is divided into 5 different parts:
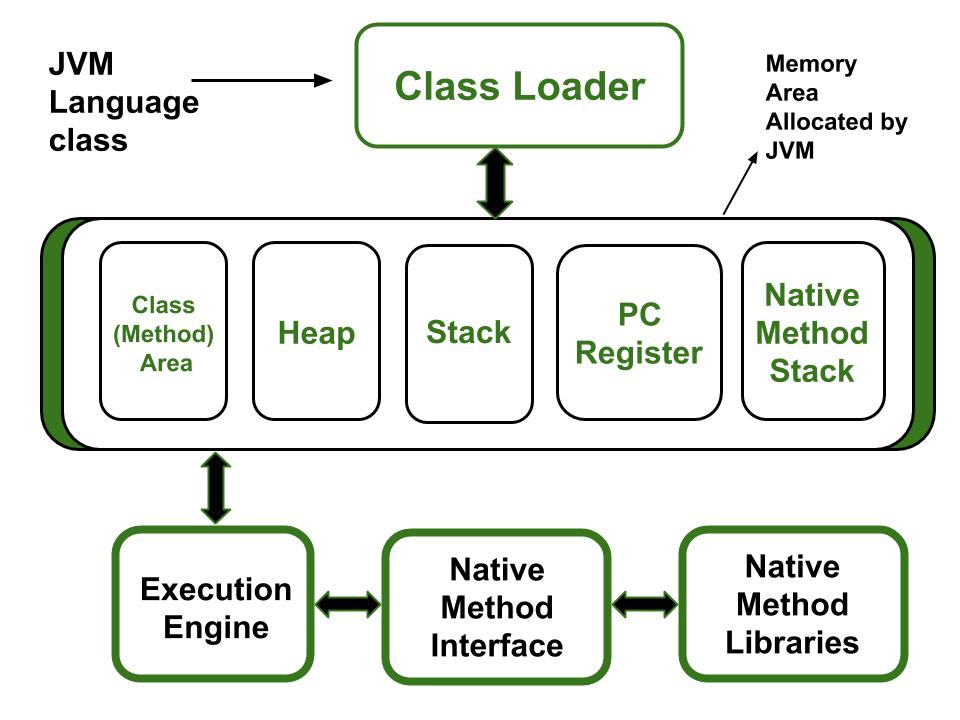
- Class(Method) Area
- Heap
- Stack
- Program Counter Register
- Native Method Stack
1. Class (Method) Area
- The class method area is the memory block that stores the class code, variable code(static variable, runtime constant), method code, and the constructor of a Java program. (Here method means the function which is written inside the class). It stores class-level data of every class such as the runtime constant pool, field and method data, the code for methods.
2. Heap
- The Heap area is the memory block where objects are created or objects are stored. Heap memory allocates memory for class interfaces and arrays (an array is an object). It is used to allocate memory to objects at run time.
3. Stack
- Each thread has a private JVM stack, created at the same time as the thread. It is used to store data and partial results which will be needed while returning value for method and performing dynamic linking.
- Java Stack stores frames and a new frame is created each time at every invocation of the method. A frame is destroyed when its method invocation completes
4. Program Counter Register:
- Each JVM thread that carries out the task of a specific method has a program counter register associated with it. The non-native method has a PC that stores the address of the available JVM instruction whereas, in a native method, the value of the program counter is undefined. PC register is capable of storing the return address or a native pointer on some specific platform.
5. Native method Stacks:
- Also called C stacks, native method stacks are not written in Java language. This memory is allocated for each thread when it’s created And it can be of a fixed or dynamic nature.


